Mastering Web App Creation: A Comprehensive Guide

In this digital era, web apps have become indispensable tools that power a wide array of platforms, from social media and online marketplaces to productivity tools and e-learning solutions . Whether you're an entrepreneur launching a startup or a developer yearning to build the next big thing, creating a web app is an exhilarating and rewarding journey. But, where do you begin? How do you morph your app concept into a full-fledged web app that users will adore? This guide will walk you through a step-by-step process of creating a web app from scratch.
Understanding Web Apps
A web app is a software application that employs web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to deliver a user interface and interact with server-side components. Unlike native mobile apps, which you install and run directly on a device, users can access web apps from any device with a web browser, offering convenience and accessibility.
Web apps can be static, dynamic, single-page apps (SPAs), or progressive web apps (PWAs).
- Static web apps: These are simple apps with static web pages displaying identical content for all users.
- Dynamic web apps: These are more complex and interactive, comprising server-side components that generate dynamic content based on user input and data.
- Single-page apps (SPAs): SPAs load a single HTML page and dynamically update the content based on user interaction without requiring a full page refresh.
- Progressive web apps (PWAs): PWAs are advanced web apps that use modern web APIs to provide a native-like experience, including offline support, push notifications, and home screen installation.

Web apps offer several advantages over native apps, including cross-platform compatibility, easy maintenance and updates, and lower development costs. Google Docs, Trello, and Asana are examples of popular web apps.
Creating a Web App: A 10-Step Guide
Creating a web app involves several stages, from ideation and design to development and testing. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process.
Step 1: Identify the Problem and Target Audience
Any successful web app begins with identifying the problem it aims to solve and the target audience it serves. Consider the following questions:
- What problem will my app solve?
- Who is my target audience?
- What are their pain points and needs?
- How will my app address these?
For instance, if you're developing a web app for a food delivery service, your target audience might be individuals who lack time to cook or prefer home delivery convenience. Your app should provide a seamless platform for ordering and tracking deliveries, addressing your audience's primary pain point.
Step 2: Define the Features and Requirements
Next, outline the features your app needs to serve its purpose effectively. This includes core features essential to solving the problem and additional features that enhance the user experience and differentiate your app from competitors.
Furthermore, define your web app's requirements regarding performance, security, scalability, and compatibility with different devices and browsers. Document these requirements and use them as guidelines throughout the development process.
Step 3: Sketch Out the User Interface and User Experience
Sketching out the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design involves creating wireframes and mockups of the app's layout, navigation, and visual elements. Consider how users will interact with the app to achieve their goals.
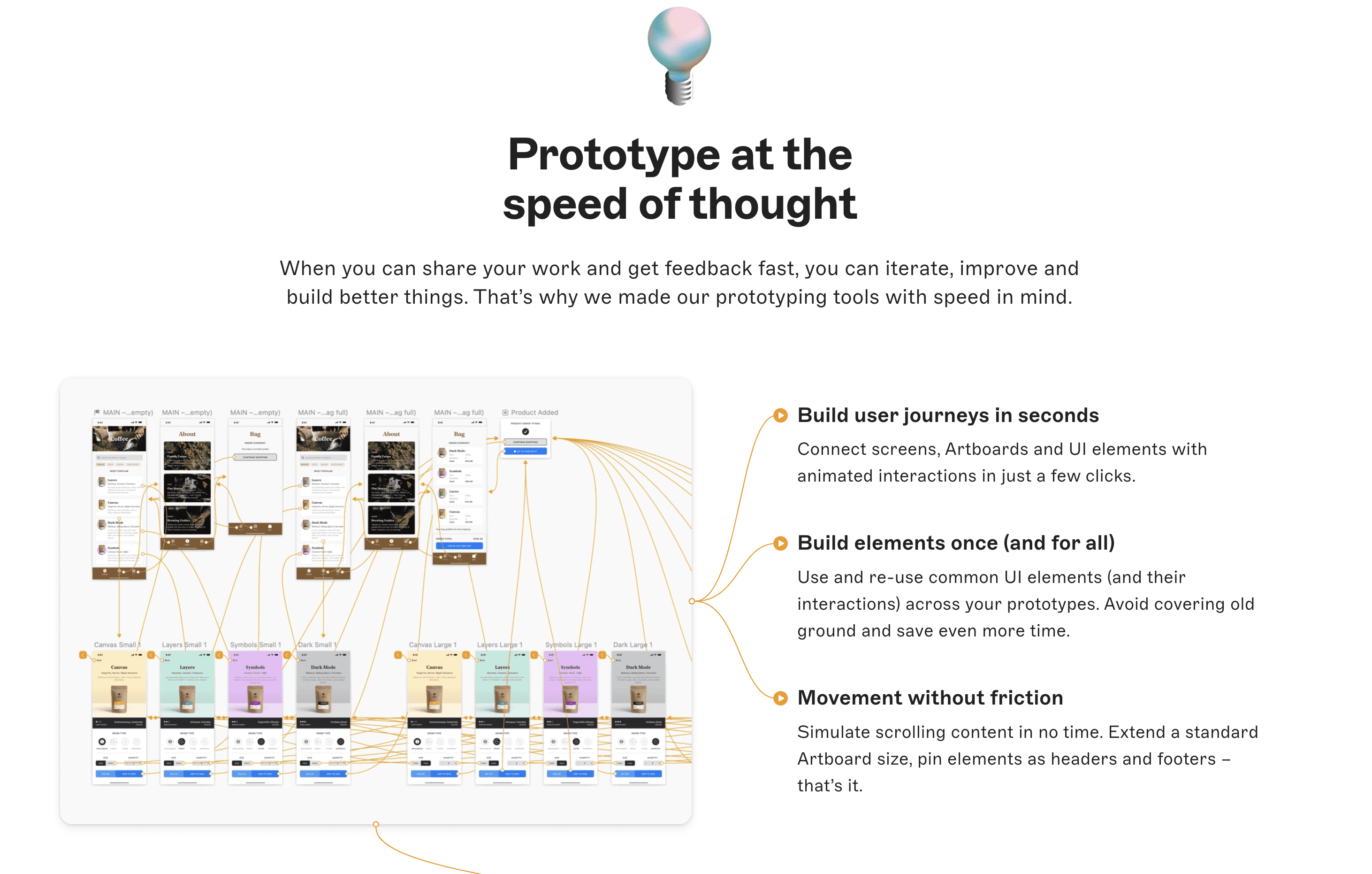
Once you've created the wireframes and mockups, gather feedback from potential users to iterate and improve the design.
Step 4: Choose the Right Programming Language and Framework
The choice of programming language and framework depends on the app's complexity, scalability requirements, and developer availability. Popular programming languages for web development include JavaScript, Python, PHP, Ruby, and Java.
Additionally, you'll need to select a web development framework like React, Angular, Vue, Django, Laravel, or Ruby on Rails.
Step 5: Set Up the Development Environment and Tools
To build a web app, you need to set up the correct development environment and tools. This involves selecting a code editor that suits your needs, such as Visual Studio Code , Sublime Text, or Atom, and installing the necessary dependencies for your chosen programming language and framework.
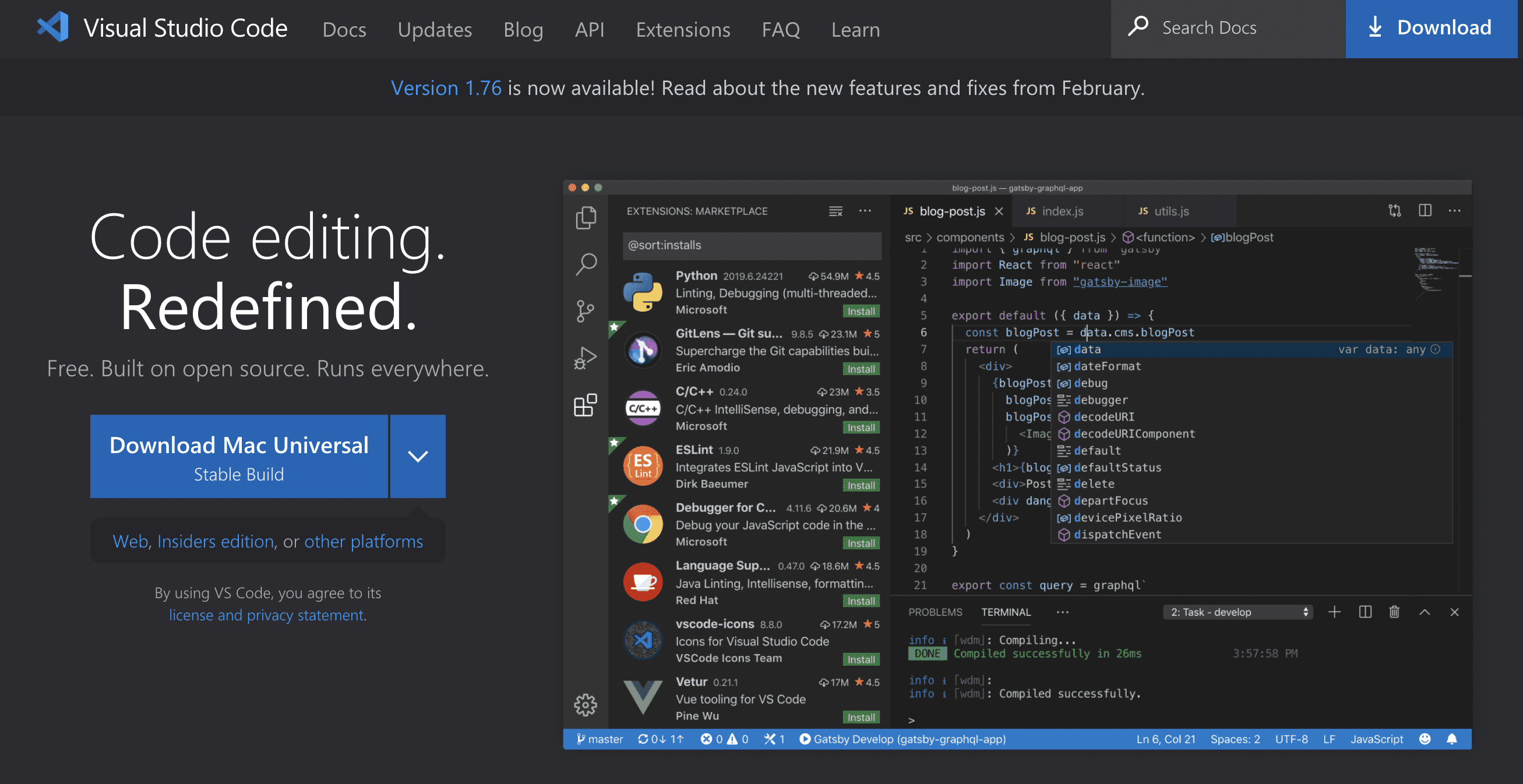
Step 6: Develop the Front-end Interface and Design
The front-end development involves creating the visual elements, layout, and interactivity of your app's user interface (UI) using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Consider using a front-end framework such as React, Angular, or Vue to speed up the development process.
Step 7: Develop the Back-end Logic and Server-side Components
After the front-end development, focus on the back-end logic and server-side components. This involves creating the code and infrastructure that handle the app's business logic, data storage, and communication with the front end.
Step 8: Test the Web App
Before deploying your web app, test it for functionality, performance, and security. Use tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights to identify areas for improvement.

Step 9: Deploy the Web App
After testing, deploy your web app to a hosting service and configure the server and database. You can choose a server provider like AWS, Google Cloud, or Heroku.
Step 10: Monitor User Feedback and Engagement
Once your web app is live, gather user feedback and monitor user engagement. This feedback can help you identify issues and new features that users would like to see, helping you continuously improve the app.
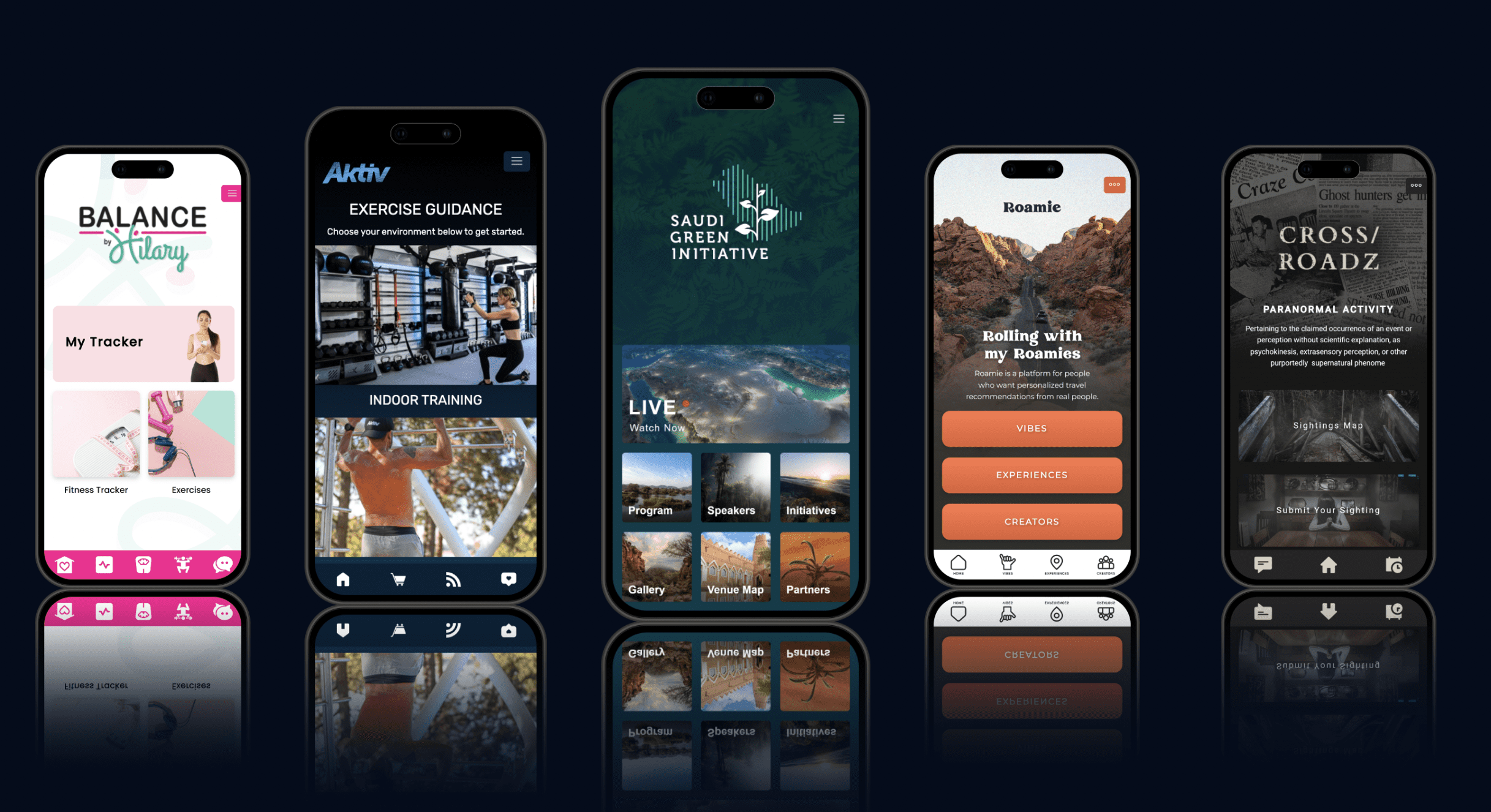
Web Apps vs. Mobile Apps: A Comparison
While web apps and mobile apps share similarities, they also have key differences. Understanding these can help you choose the best option for your project.
Web apps run on web browsers like Google Chrome or Safari, and they're accessible on any device with an internet connection. On the other hand, mobile apps run natively on a mobile device and require installation from an app store.
Conclusion
Building a web app requires careful planning, design, development, and deployment. By following the steps outlined in this guide, and continuously monitoring and improving your app, you can create a successful web app that provides value to your users.
Whether you're building a web app or a mobile app, focusing on your users is key. Prioritize user feedback and engagement, and continuously improve your app based on the data and feedback you receive. This approach ensures your app stays relevant and valuable to your users, helping you achieve your business objectives.